Complete O/L notes biology: CHP.5 AMOEBA
Complete O/L notes biology: CHP.5 AMOEBA
CHAPTER FIVE
5.0. AMOEBA
5.1. Classification of amoeba
Kingdom: protoctista
Phylum: Rhizopoda
Class: sarcodina
Genus: proteus
Scientific name: Amoeba proteus
Common name: Amoeba
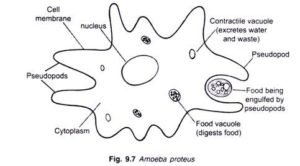
Fig: structure of amoeba
- Amoeba are free living unicellular microscopic organisms. They have an indefinite shape. They are colorless and they are jelly like in form (they cannot be seen with the naked eyes and they are 0.1 mm. their whole body is surrounded by a plasma membrane (plasmalemma) inside the body as a clear plasma gel collide cytoplasm. It is a semi solid and further inside there is a plasmas oil ectoplasm. It has a nucleus many food vacuoles and a contractile vacuole it forms pseudopodia which act as false feet.
- The plasma (cell membrane) contains the cytoplasm and it allows the passing of H2 and O it is selectively permeable cytoplasm. It is made up of ectoplasm which is jelly like and the endoplasm which help to give the organism its shape and they help the organism during locomotion when the organism forms pseudopodia
- Nucleus: it contains the hereditary materials called chromosomes and it controls the activities of the cell
- Contractile vacuoles: the contractive vacuole forms an organ which is used for excretion of water and another wastes
- Food vacuoles: they contain food that is undergoing digestion
- Pseudopodia: this is used for locomotion
5.2. Processes that amoeba carries out
Nutrition: Amoeba feeds holozoic ally i.e. it takes in food digest within body and then absorbs
When amoeba carries in contact with food particles. It sends out pseudopodia which surrounds the food particle with some water to form a vacuole. The taking in of food is called ingesting. The amoeba needs by englutting therefore particle in a process known as pinocytosis. the food in the food vacuole is digested by enzymes and the digested material is absorbed and after that it diffuse in the cytoplasm.
The undigested material is sent out along with water through the contractile vacuole. The sending of undigested material is called egestion.
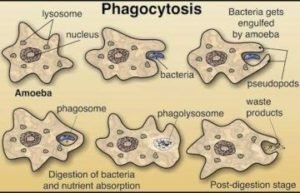
Fig: feeding in amoeba
5.3. Respiration in amoeba
Amoeba is a unicellular organism and so respiration is by simple diffusion i.e. oxygen simply diffuses into the organism and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the organism
5.4. Excretion and osmoregulation in amoeba
Amoeba use the contractile vacuole to send out water and digested food. This is in fresh water amoeba. Marine amoeba has no contractile vacuole.
5.5. Habitats in amoeba:
Amoeba will move away from touch strong light from a touch. It will also move away from high temperatures from acids; poisonous chemicals but it will move towards food.
5.6. Reproduction in amoeba
Amoeba reproduces asexually by binary fission and by sporulation
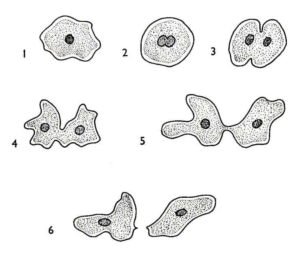
Fig: reproduction in amoeba
5.6.1. Binary fission in amoeba
in this case, the nucleus divides, the cytoplasm divides and two organisms are formed.
5.6.2. Sporulation in amoeba
During unfavorable conditions such as drought the amoeba forms a thick covering around itself then becomes what is called a cyst. The amoeba inside will divide several times to become spores. When the season becomes favorable again, the amoeba breaks open and each spore becomes a new amoeba.
5.7. Locomotion in amoeba
Amoeba moves continuous formation and redrawer of the pseudopodium in the direction of movement. It appears to be flowing and this is called amoeboid movement when the amoeba moves to the fluid axopodium flows into the advancing pseudopodium as the same time the opposite end of the organism withdraws a new pseudopodium is formed and the process continues
5.8. Biological importance of amoeba
- Many multicell organism evolved from unicellular ones
- Amoeba can cause diseases e.g. amoeba histolyka
- In streams, amoeba cleans off dirt and dead organisms
5.9. Difference between bacteria and amoeba
| bacteria | amoeba |
| Has a defined nucleus | Has a nucleus |
| Has a protein cell wall | Has no cell wall |
| Has no contracted vacuole | Has a contracted vacuole |
| May move with the help of flagella | Move with help of pseudopodium |
| Has mesosomes for production of energy | Has a mitochondrion |