Lesson 24: DESERT LANDSCAPE
A desert is generally a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and consequently living conditions are hostile for plants and animals.
Characteristics of deserts
- The vegetation cover is very scanty.
- Soils are very poor, dry and loose.
- Low humidity.
- Low amount of rainfall.
- The area is very dry and arid.
Location of hot deserts
Hot deserts are located between latitude 15°-35° north and south of the equator.
- In Africa we have the Sahara, the Namib and the Kalahari Desert.
- In India we the Tar Desert ().
- Atacama Desert (South America).
- The Mohave Desert (USA).
- The great Australian desert (Australia).
Reasons for occurrence of hot desert
- Interior of continent: areas that is located in the interior of continents ere usually far from water bodies that bring moisture to form precipitation.
- Rain-shadow belts of mountainous areas: in this case, the mountains act as a barrier to rain bearing winds. Causing one side to be deprived of moisture.
- Western margins of continents: they correspond to coastal area where winds are offshore. Moisture that could condense to form rainfall is instead carried to the interior of the continents.
- Subtropical pressure belts: these are large high pressure belt areas e.g. the tropic of cancer and of Capri cone. Where air is sinking from above the surface and there is low humidity.
Wind actions in deserts
- Abrasion: this is the process of wind erosion where by wind loaded with sand grains erodes rocks by grinding against its walls.
- Deflation: it is the process of wind erosion which involves the removing, lifting, and carrying away of dried particles by wind leaving behind depressions known as blow outs.
- Attrition: it refers to the wear and tear of sand particles while they are being transported.
- Erosional features of wind action
- Rock pedestal: these are isolated mushrooms pillars of rocks with relatively broad tops and narrow bases found in the hot desert.
They are formed when rocks masses are made up of alternating hard and soft rocks lay on the path of the winds through the process of abrasion. So winds remove the softer rocks faster than the harder rocks. Since abrasion is greater nearer the surface, the base of the mass rock is more ascarvated living behind a mushroom shaped rock pillars.
ROCK PEDESTRAL
- Deflation hollow: these are large circular depressions found in desert environment.
They are formed when wind continuously blow off loose materials from desert surfaces leaving behind.
NOTE: in a case where the depression reaches the water table, the deflation stops because it is difficult for wet soil to be transported by wind.
- Ventifact and dreikanters: they are sand polished pebbles derived from mechanically weathered rocks which lie along the path of the wind.
Ventifacts are formed when rock boulders are subjected to abrasion by prolonged wind actions.
Dreikanters are formed when a ventifact is abraded on as many as three sides.
- Wind depositional features
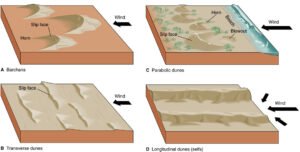
- Dunes: these are heaps of sand deposited by wind when the wind meets an obstacle.
There are two common types:
- Barchans: these are moon or crescent shape heaps of sand that lie at right angles to the prevailing winds.
They are formed when wind meets an obstacle such as a piece of rock boulder. The sand transported by the wind forms heaps on the wind ward side and then slips down on the lee ward side forming sharp edges.
- Seif dune: these are long narrow and steep sided ridges of accumulated sand separated from each other by farrows that have swept clear sand by edges. Seif dunes always lie parallel to the direction of the prevailing winds.
Resources of the hot desert
- Some desert landforms are very attractive. These attracts tourist.
- Abundant sunlight which are harnessed to form solar energy.
- Fertile soils in the Oasis.
Challenges of the hot desert
- Extreme temperatures.
- Very scanty vegetation.
- Poor loosed soils.
- Water scarcity.
Adaptations
- The plants trees are drought resistant.
- Desert inhabitants dig wells and bore holes to serve as water catchments.
- Most desert inhabitants wonder from place to place with their animals in search of pasture.