Lesson 21: RAINWATER ACTION ON LIMESTONE LANDSCAPE
Limestone is a sedimentary rock of organic origin derived on the accumulation of coral and shell in the sea. It is made up of calcium carbonate.
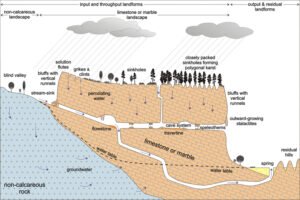
General characteristics of limestone regions
- The rocks contain 80% calcium carbonate.
- The rocks are well jointed.
Features produced in limestone regions
- Surface features
- Doline: this is a funnel-shaped depression found in limestone region. It may origin from the solution of a joint. It varies from ten metres to one hundred meters in diameter.
- Uvala: it is a funnel shaped depression of several km in diameter found in a limestone region. It varies from 100 meters to seven km
- Polje: it is a large steep sided depression with flat floors found in limestone regions. It results from a mergence of several uvulas’.
Problems of limestone regions
- Waste disposal.
- Water scarcity.
- Poor agriculture due to dry soils.
- Problems of engineering projects.
Importance
- Used in the iron industry to separate iron from other impurities.
- Used in decoration.
- They attract tourist.
- They are used in industries to produce chalk.
Lesson 22: RUNNING WATER (ACTION OF WATER ON THE LANDSCAPE)
The long profile of a river
Definition of terms:
- A river is a natural body of water that flows in a definite channel toward a sea or lake.
- The long profile of a river is cross section of a rive r showing it stages from the source to the mouth where it enters the sea.
There are three stages involved in the river course. I.e.
- Upper course (youthful stage)
- Middle course (mature stage)
- Lower course (the old stage)
- Features produced at the upper course of a river
At this stage, the gradient is steep and vertical erosion is dominant, small volumes of water. The land forms produced here are mainly erosional.
- V-shaped valley: it is a steep sided and narrow bottom valley common in upper course of a river. It has a v- shape.
It is caused by vertical corrosion on the valley floor. THE VALLEY size is widened by both weathering and mass movement to produce a goerge.
- Interlocking spurs: as erosion is still vertical, the river tends to twist and turn round had rocks searching for the path of the less resistant rocks. This protrusion of hard rocks tends to interlock, hence interlocking spurs.
- Water fall: This is a steep or vertical descent in the course of a river. IT MAY BE CAUSED by the following ways.
- Where a hard rock overlies a soft rock
- Where faulting had occur across the river bed
- Where water plunges down the age of a plateau.
Others erosional features are rapids, potholes etc.
- Features produced in the middle course of a river.
It is characterised by vertical and lateral erosion, gentle sloping slopes larger volume of water.
- River cliffs and slip off slopes: as the river wind between the interlocking spurs, lateral erosion takes place on the concave side while deposition takes place on the convex side.
On the concave bend where erosion is dominant, a river cliff is produced while on the convex bend, slip off slopes is produced.
- Features produced in the old stage:
- Braided river: this is where so much materials is deposited on the river bed so that the river is broken up into channels .This is a situation known as river braid.
- Flood plain: at the old stage, the main work of the river is to deposit materials. Huge sediments are deposited at the adjacent low lying area. This deposition gradually spreads to form a flood plain.
- Meanders: it is a curved loop like bend in the course of a sluggish river. These are series of bends in a river bend. The irregularities of the river make the river to swing from sides to sides forming a meander.