In this Article we are going to explore the Variation of intermolecular force with separation between particles, this is the continuation of our previous Article all that under the topic Matter in Physics.
Intermolecular Force

When both particles are apart, the forces between them are too weak to be significant. When closer they attract each other. If the separation is reduced further, it gets to a position where attractive force is balanced by the repulsive force. The separation is both the intermolecular or inter atomic distance or atomic radius which is about 10-9m
Beyond this separation, repulsion dominates the attractive forces. A further attempt to reduce this separation meets with a higher repulsive force. This behavior can be represented on a graph.
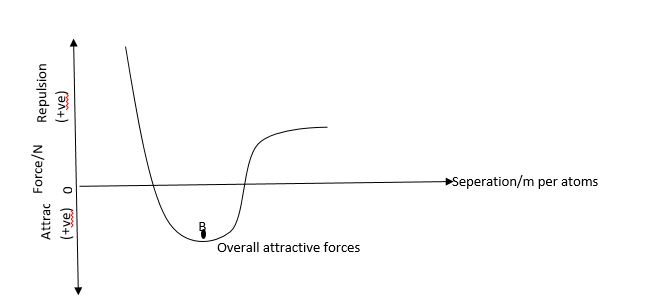
The repulsive force which acts in the direction of increase r in increase to B and then decrease with distance form B the 2 forces are equal at R. this reason, r0 is called the equilibrium separation is equal
to the distance between the centers of the 2 atoms in an up stretched metal wire. Any slight increase or r from r0 will lead to the force between the atoms restoring to their equilibrium spacing thereby causing the atoms to correlate about the equilibrium position. This implies Hook’s Law is obeyed in this region that is the force constant K is related to the force by the equation.

In the Next Article we shall be exploring the Relationship and Intermolecular potential energy and Particle Separations.












Kenne kouatedzo Rahim
October 1, 2024
It's precise and concise