Complete O/L notes biology: Plasmodium
CHAPTER SIX
6.0. PLASMODIUM
6.1. Classification of plasmodium
Kingdom: protoctista
Phylum: Rhizopoda
Class: Aconoidasida
Scientific name: plasmodium
Plasmodium belong to a phylum Rhizopoda. They spread most of their life in mosquitoes and they rest in man where it gets into the red blood cells. Multiplies in it and destroys.
6.2. Methods of transmission
Plasmodium is transmitted from an infected person to an uninfected person through a bite from a female anopheles’ mosquitoes. The female anopheles feeds on the blood for the development of eggs and when it takes the blood to malaria positive which have been developing in the salivary glands in the mosquitoes are injected into the blood stream of the uninfected person which it takes some blood chemicals in the salivary gland prevents the blood from clotting.
The plasmodium feeds on the cytoplasm of the red blood cell and so destroys the red blood cell to cause anemia.
///////////////////////diagram of plasmodium//////////////////////////////
6.3. Signs and symptoms of malaria
- Fever
- Shivering
- Headache
- Joint palms
- Wick nose
- Loss of weight
- Loose appetite
In the cause of cerebral malaria, there is a lot of anxiety and the patients behave abnormal when taking treatment for malaria make sure you take the does.
6.4. Effects of plasmodium
- The parasite feeds on the red blood cells causing anemia
- Which the red blood cells are destroyed they over work the spleen
- The parasite produces toxic substance leading to fever
- Malaria causes headache
- Sometime malaria causes conversion in children
- Pregnant women may pass the malaria to the unborn baby
- The Female anopheles’ mosquito is a naissance when its humming in one’s ears
- Mosquitoes bites can be painful and it sometimes causes wounds.
6.5. Prevention and control of malaria
- Use insecticides to kill them
- Clear all grass and bush to destroy the breathing places of the mosquitoes
- Burry all empty tins to destroy their breathing places
- Fishes may be placed on pounds so that they feed on them and pupae of the mosquitoes
- Drain all standing water or till soil to destroy the breathing places
- Sprinkle out or till soil to destroy the breathing place
- Sprinkle oil or kerosene on standing water to suffocate the larvae and pupae
- Always close the doors and windows before 5pm to prevent mosquitoes from entering the house
- It is possible put nets on the windows and beds to prevent mosquitoes
- Use anti malaria drugs and take at full dose.
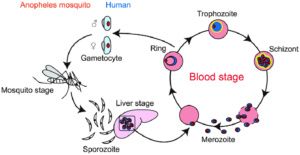
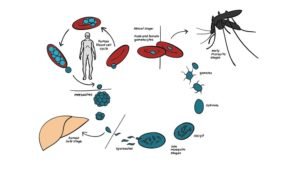
6.6. Life cycle of malaria
When the female anopheles mosquito sucks blood from an infected person, it takes in the malaria parasite.
Before a mosquito takes up blood, it will release a chemical when prevent the blood from clothing in the mosquito.
The parasite developed in the salivary gland of the mosquito to parasite which can infect a healthy person when the mosquitoes bites him/her, the parasite develop in the mosquito to become sporozoites. These can be injected into a healthy person and he would become infected. In the infected person the sporozoites are carried by the blood to the liver and the develop into schizonts. The schizonts are multinuclear and the develop into merozoites in the liver cells when schizonts develop into merozoites the liver cell and they are released into the blood stream. This cycle which takes place in the liver is called the pre-enterocytic cycle. The process where sporozoites develop schizonts is called schizogony.
Sporozoites
Liver
Schizogony
Schizonts
Trophozoites
Merozoites
When schizonts develop in merozoites and this merozoites which develops from the red blood cell where they develop into trophozoites. This trophozoites scan further develop into schizonts and finally again to merozoites cell this happen in the red blood cell.
////////////////////////diagram from sporozoites ///////////////////////////////