THE CELL CONCEPT
The cell concept
Introduction: The cell was discovered by the scientist called Robert Hooke who was studying a tree cork cells using a lower power microscope in the year 1665. He saw that the cork was made up of several tiny units and he called them cells coming from the Latin word “cella” meaning “small room”.
Definition: A cell is the basic (smallest) structural and functional unit of living things.
Unicellular organisms are only one cell. E.g. amoeba, yeast etc.
Multicellular organisms have more than one cell. E.g. plants and animals.
Types of cells
There are basically two types of cells classified based on whether or not they have membrane bound organelles or membrane bound nucleus. These cells are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells respectively.
- Prokaryotic cells
These are cells that lack membrane bound nucleus and membrane bound organelles. E.g. Bacteria.
Characteristics of prokaryotes
- Small (1-10 μm)
- DNA circular, unbounded
- Genome consists of single chromosome.
- Asexual reproduction common, by mitosis.
- No general organelles
- Most forms are singular
- Eukaryotic cells
These are cells having membrane bound organelles and membrane bound nucleus. E.g. plant cell, animal cell, Fungi and protozoans. Etc.
Characteristics of eukaryotes
- Large (100 – 1000 μm)
- DNA in nucleus, bounded by membrane
- Genome consists of several chromosomes.
- Sexual reproduction common, by mitosis and meiosis
- Mitochondria and other organelles present
- Most forms are multicellular
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| Relatively small | Relatively large |
| Mainly unicellular | Mainly multicellular |
| Fewer organelles | Many organelles |
| Nucleus absent | Nucleus present |
| E.g. Bacteria | E.g. Plants, Fungi and animals |
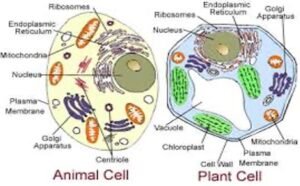
Functions or parts of a typical eukaryotic cell
- Cell wall: It gives cells its shape. It also allows substances to move in and out of the cell.
- Cell membrane: It also allows substances to move in and out of the cell. E.g. food and water etc
- Mitochondrion: It is called the power house of the cell. It provides energy for the cell.
- The nucleus: It controls all activities of the cell and it is used in reproduction.
- Cytoplasm: It houses (keeps all organelles in the cell in their positions).
- The vacuole: It stores food and regulates the water content in the cell.
- Chloroplast: It produces chlorophyll, while they help plants manufacture their food.
- Starch granule: They store food.
- Glycogen granule: They store food.
Differences between plant and animal cells
Other differences
| Plant cell | Animal cell |
| Large centrally located vacuole | Many small vacuoles |
| Have a fixed shape | Has no fixed shape |
| Small cytoplasm | Large cytoplasm |
| Usually large | Usually small |
more notes at GCE REVISION and kawlo application










